Testosterone is often referred to as the “male hormone,” but its importance goes far beyond masculinity. It plays a critical role in a man’s physical, mental, and emotional well-being. While it’s most commonly associated with muscle building and libido, testosterone is involved in numerous processes that keep the body running optimally.
What Is Testosterone?
is a hormone that belongs to a class of androgens, often referred to as “male hormones.” While both men and women produce testosterone, it is found in significantly higher levels in men and is primarily produced in the testicles. A small amount is also produced in the adrenal glands.
Key Facts About Testosterone

- It begins to rise during puberty and peaks during adolescence and early adulthood.
- After the age of 30, testosterone levels tend to decline by about 1% per year, a natural part of aging.
- Low testosterone, also known as hypogonadism, can lead to several health issues if not addressed.
Why It Matters:
Testosterone isn’t just about looking or feeling “manly.” It impacts almost every system in your body, making it vital for your overall health.
The Roles of Testosterone in Men
Testosterone plays a multifaceted role in a man’s body. Let’s break it down into its key functions:
Sexual Health and Reproduction

Testosterone is often most recognized for its role in male sexual health. It regulates libido (sex drive), supports sperm production, and influences erectile function.
Key Insight:
Low testosterone levels can lead to a decrease in sexual desire, reduced fertility, and erectile dysfunction.
Muscle Growth and Bone Density
Testosterone is essential for building and maintaining muscle mass and strength. It also helps maintain bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis as men age.
Why It Matters:
Low testosterone can result in muscle weakness and brittle bones, making physical activities more challenging.
Fat Distribution
The hormone also regulates fat distribution in the body. Men with healthy testosterone levels tend to have lower body fat percentages, while low testosterone can contribute to increased fat storage, particularly around the abdomen.
Mood and Mental Health
Testosterone affects mood, energy levels, and mental clarity. Healthy levels are associated with reduced risk of depression, improved focus, and greater confidence.
Fun Fact:
Some studies suggest that low testosterone can increase irritability and feelings of fatigue, commonly referred to as “male menopause.”
Red Blood Cell Production
Testosterone stimulates the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow, which are essential for transporting oxygen throughout the body.
Why It’s Important:
Low red blood cell levels can lead to anemia, causing fatigue and weakness.
Hair Growth
During puberty, testosterone triggers facial, chest, and body hair growth in men. It also influences the thickness and pattern of hair throughout a man’s life.
Transition Tip:
While hair loss is often genetic, low testosterone can contribute to thinning hair in some men.
Signs of Low Testosterone

Recognizing the signs of low testosterone is crucial for addressing it early. Common symptoms include:
- Decreased libido or sexual performance.
- Reduced muscle mass and strength.
- Increased body fat, particularly around the waist.
- Fatigue or low energy levels.
- Mood changes, such as irritability or depression.
- Difficulty concentrating or memory problems.
- Thinning body and facial hair.
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Physical Activities to Boost
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to naturally increase testosterone levels. Certain types of exercises are particularly beneficial.
1. Strength Training
Lifting weights is a proven method to boost testosterone production. Compound movements that target multiple muscle groups are especially effective.
Best Exercises:
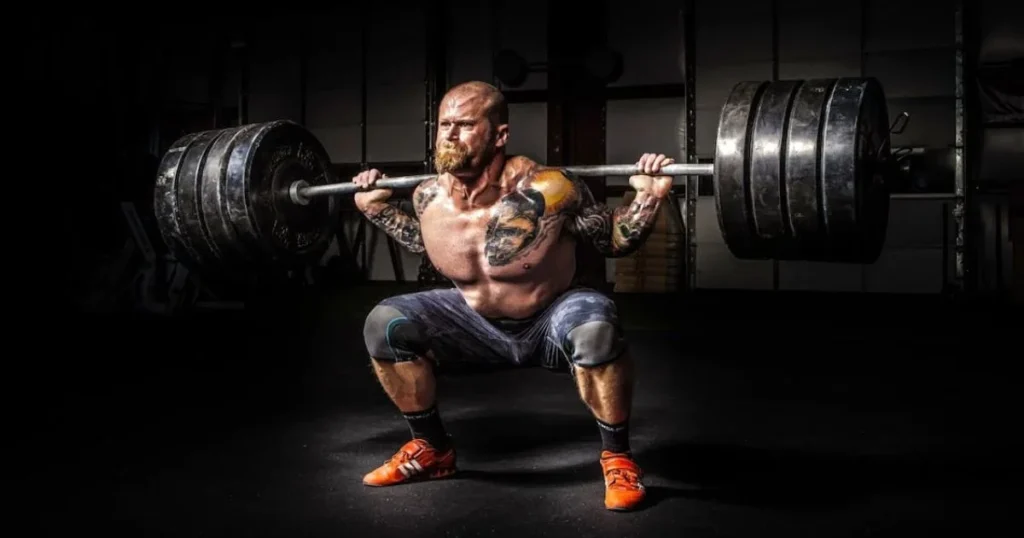

- Squats
- Deadlifts
- Bench presses
- Pull-ups
Why It Works:
Strength training triggers the release of testosterone to repair and grow muscles. Aim for 3–4 weightlifting sessions per week for optimal results.
2. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief rest periods. It’s not only great for burning fat but also for increasing testosterone levels.
Example HIIT Workout:
- Sprint for 30 seconds.
- Rest for 90 seconds.
- Repeat for 8–10 rounds.
Key Insight:
HIIT stimulates the production of anabolic hormones, including testosterone, while improving overall cardiovascular health.
3. Moderate Cardio
While excessive cardio can lower testosterone levels, moderate cardio can improve circulation, reduce stress, and support hormonal balance.
Suggestions:
- Jogging
- Swimming
- Cycling
Transition Tip:
Balance cardio with strength training to avoid overtraining, which can lead to a drop in testosterone.
4. Active Recovery
Activities like yoga and stretching might not directly boost testosterone, but they help reduce cortisol levels. Cortisol, a stress hormone, can suppress testosterone production.
Why It’s Beneficial:
Reducing stress through active recovery allows testosterone levels to stabilize and thrive.
related : Impact of Sex with the Right Partner on Mental Health
The Role of Healthy Eating in Testosterone Production
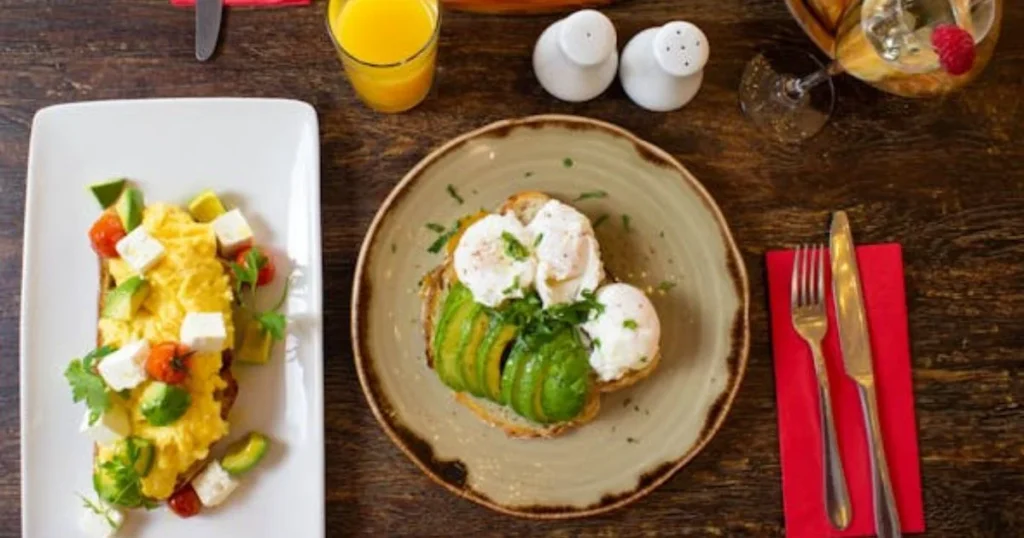

Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining and boosting testosterone levels. The right foods can provide the nutrients needed for optimal hormone production.
Foods Rich in Healthy Fats
Testosterone production relies on cholesterol, so consuming healthy fats is essential.
Best Sources of Healthy Fats:
- Avocados
- Nuts (almonds, walnuts)
- Olive oil
- Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel
Key Insight:
Dietary fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, are vital for supporting testosterone synthesis.
Protein-Packed Foods
Protein helps maintain muscle mass and regulates hormone levels.
Top Protein Sources:
- Eggs
- Lean meats like chicken and turkey
- Greek yogurt
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas)
Why It’s Important:
Protein-rich foods provide amino acids essential for muscle repair and hormonal balance.
Zinc and Magnesium-Rich Foods
Zinc and magnesium are minerals directly linked to testosterone production.
Foods High in Zinc:
- Oysters
- Beef
- Pumpkin seeds
Foods High in Magnesium:
- Spinach
- Dark chocolate
- Almonds
Key Insight:
A deficiency in these minerals can lead to lower testosterone levels, so incorporating them into your diet is crucial.
Carbohydrates for Energy
Carbs are often misunderstood, but they play a role in sustaining energy levels during workouts and aiding recovery.
Healthy Carb Sources:
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Sweet potatoes
- Whole-grain bread
Transition Tip:
Focus on complex carbs for sustained energy without the sugar spikes.
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can negatively impact testosterone levels, so it’s best to consume them in moderation.
Avoid or Limit:
- Processed foods (high in trans fats).
- Excessive sugar.
- Alcohol (especially in large quantities).
Why It Matters:
A poor diet can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to lower testosterone production.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Testosterone Levels

In addition to physical activity and healthy eating, certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve testosterone levels.
1. Get Quality Sleep
Sleep is crucial for hormone production. Testosterone levels peak during deep sleep, particularly REM sleep.
Recommendation:
Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night to optimize hormone levels.
2. Reduce Stress
Chronic stress increases cortisol levels, which can suppress testosterone production.
How to Manage Stress:
- Practice mindfulness or meditation.
- Engage in hobbies that bring joy.
- Avoid overcommitting to reduce burnout.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity is linked to lower testosterone levels, so maintaining a healthy weight is essential for hormonal balance.
Key Insight:
Losing excess fat, particularly around the abdomen, can naturally boost testosterone.
Testosterone is an essential hormone that influences nearly every aspect of a man’s health, from physical performance and mental clarity to emotional well-being. By incorporating regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet, and making healthy lifestyle choices, men can naturally maintain and even increase their testosterone levels.
It’s never too late to start prioritizing your health. With the right strategies and a proactive approach, you can harness the power of testosterone to feel stronger, more energetic, and confident at every stage of life.






1 Comment
Your articles are extremely helpful to me. Please provide more information!